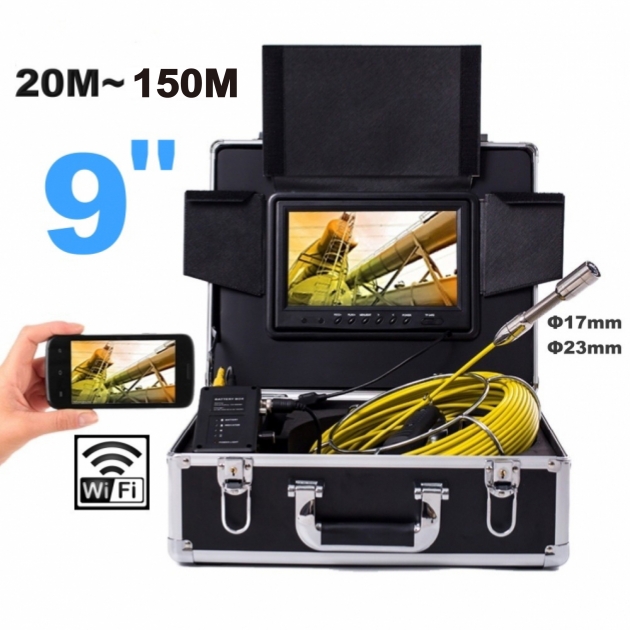
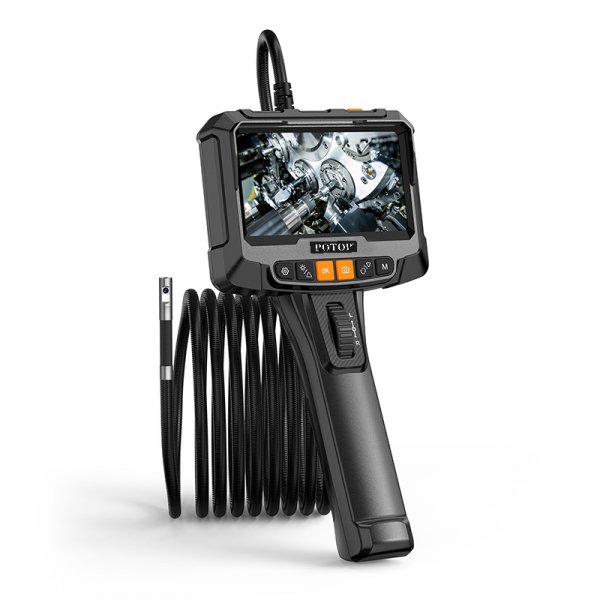
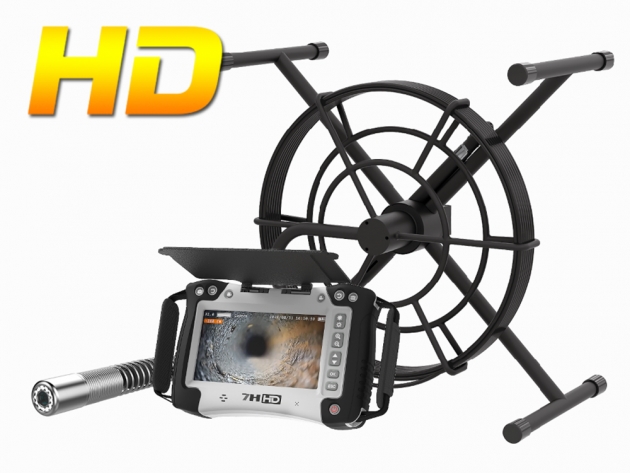
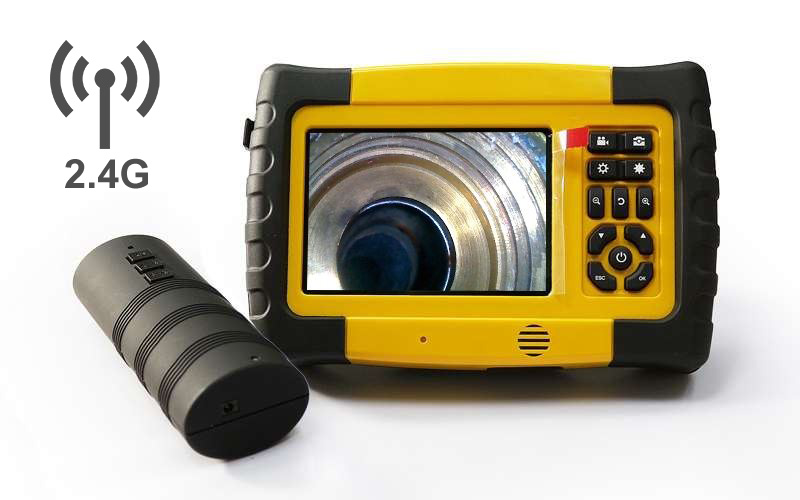
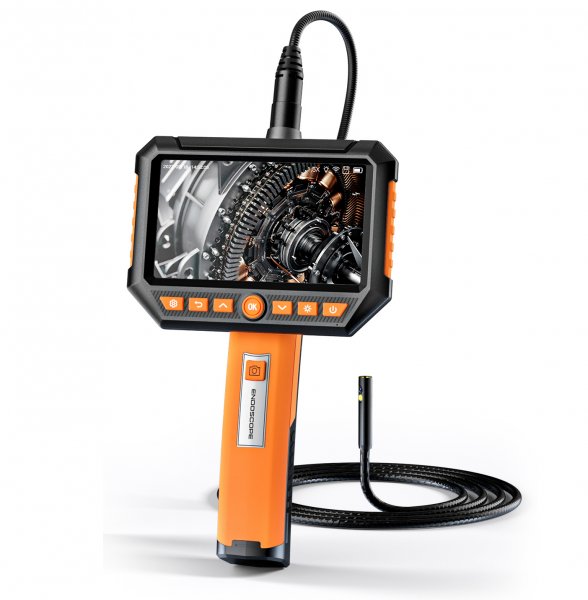
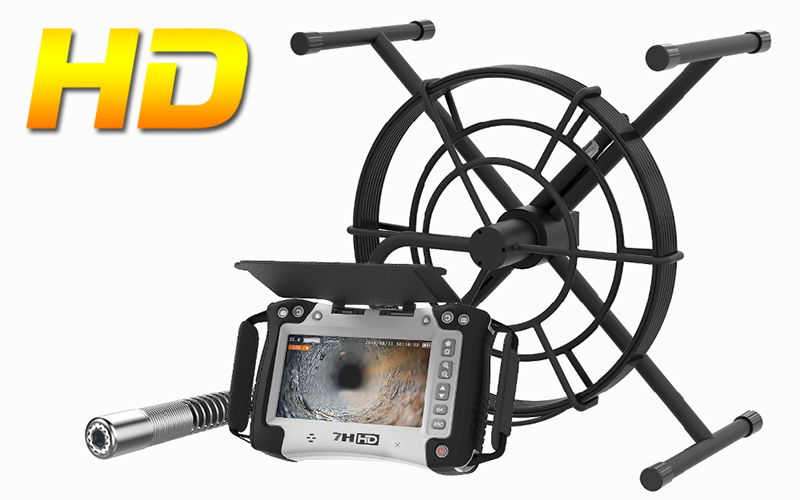
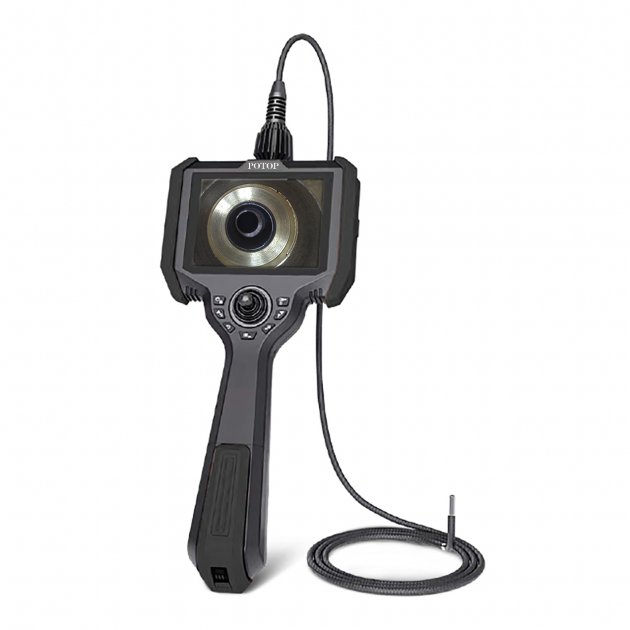
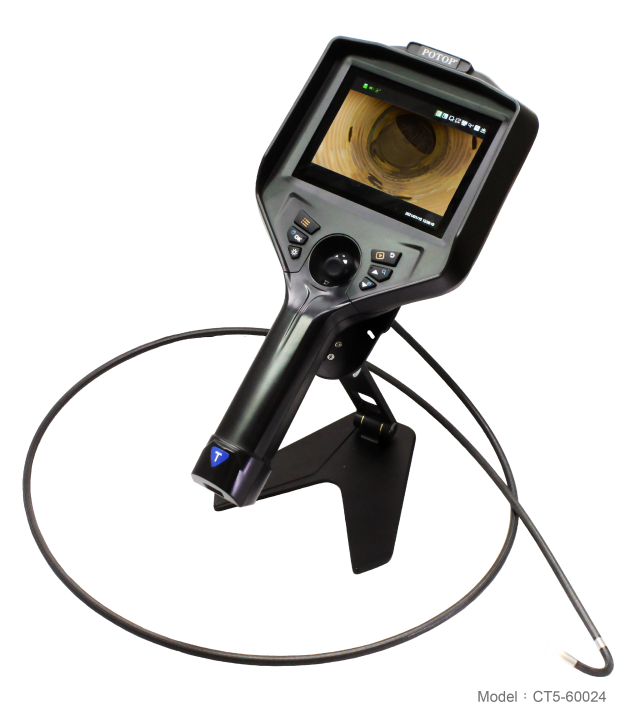
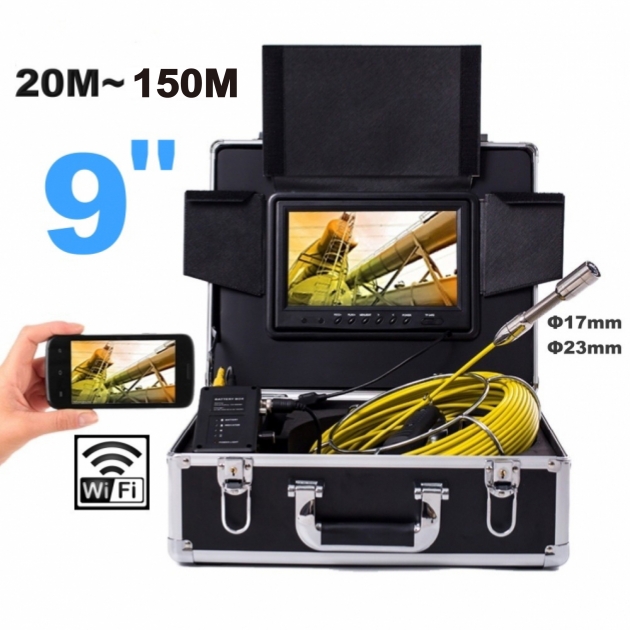
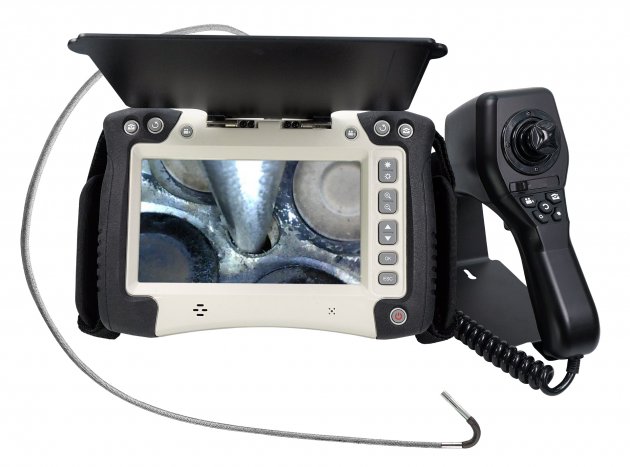
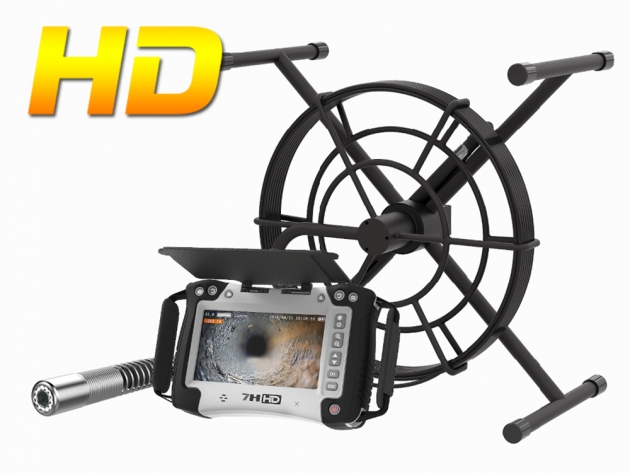
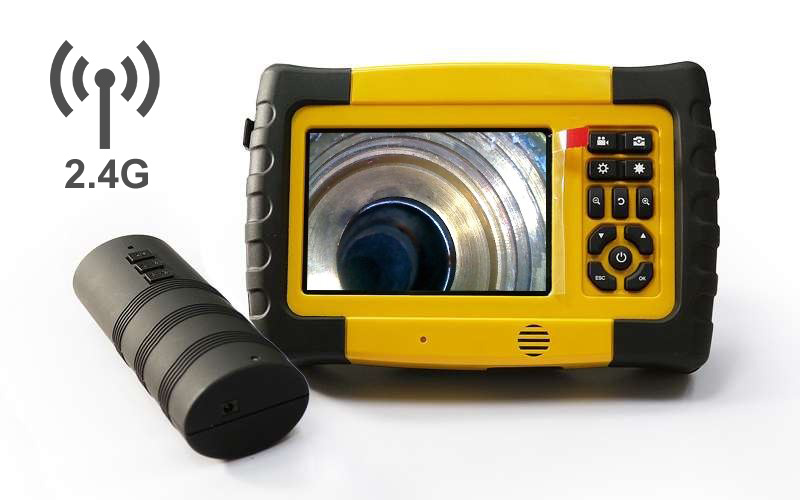
A professional-grade borescope inspection camera is an essential tool for modern inspections. By allowing technicians to visually explore narrow or concealed spaces without dismantling equipment, it not only shortens troubleshooting time and lowers repair expenses, but also enhances workplace safety. In addition, built-in recording and image capture functions make documentation easier, ensuring that every inspection is accurate, traceable, and reliable.
- What is a video borescope?
- Applications & Real-World Use Cases
- What is the depth of field in a borescope?
- What is the difference between borescope and endoscope?
- What is a borescope used for?
- Borescopes & Endoscopes in Inspection & Analysis Tools
- Borescope inspection
- What is a borescope camera?
- Flexible vs. Rigid vs. Semi-Rigid: Exploring Video Borescope Probe Options
- Borescope technology
- Key Features & Benefits of Modern Borescopes
- How to use a borescope?
- How much does a borescope cost?
- Choosing a Borescope: Guide and Considerations
- 6 Key Guidelines for Proper and Safe Borescope Use
- FAQs
- Choose the Right Borescope for your Application
- Find your Perfect Borescope Inspection Camera
What is a video borescope?
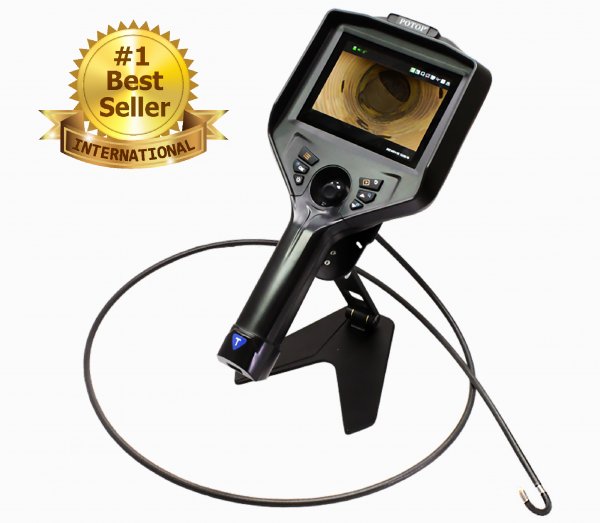
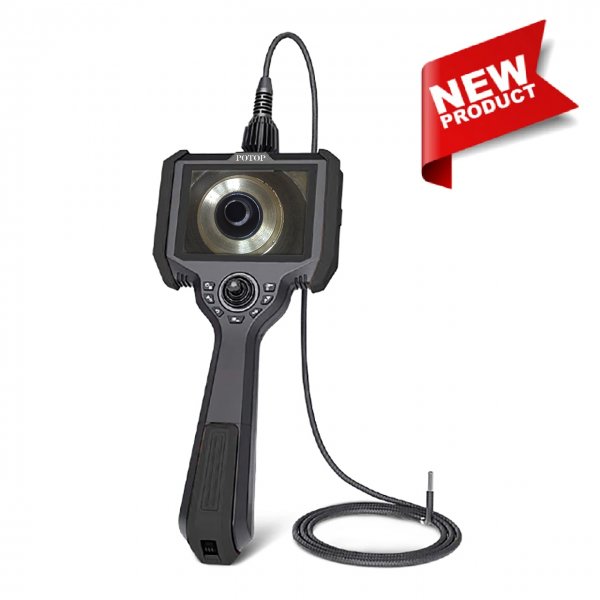
A video borescope, also known as a borescope camera, is a remote visual inspection tool commonly used in non-destructive testing (NDT). It helps users inspect narrow, hard-to-reach, or enclosed areas without the need to disassemble equipment. Unlike traditional optical borescopes, a video borescope features a miniature camera at the tip of a flexible or rigid tube. This camera sends real-time images or video through an electrical cable to a built-in screen or external display, allowing operators to clearly view internal components during inspection. Many advanced models also offer features such as articulating probes, adjustable LED lighting, high-resolution displays, and image or video recording capabilities—making video borescopes ideal for detailed inspections in industries like automotive, aerospace, plumbing, and manufacturing.
With articulating probes, adjustable illumination, and on-device recording, modern systems turn hard-to-reach inspections into fast, repeatable workflows for automotive, HVAC, plumbing, and industrial machinery.
Overview of Borescope Types
In the realm of remote visual inspection, borescopes come in various forms - rigid, semi-rigid, and flexible, each catering to specific inspection needs. Rigid borescopes, known for their clarity and durability, are best suited for straight pathways where flexibility is not required. On the other hand, flexible borescopes, often referred to as fiberscopes, offer unparalleled access to serpentine and hard-to-reach areas, albeit at a higher cost and with slightly compromised image quality. Semi-rigid borescopes strike a balance between the two, offering better maneuverability than rigid models without sacrificing much on image sharpness.
Articulating vs. Non-Articulating Borescopes
There are two primary categories of video borescopes: articulating and non-articulating.
- Articulating borescopes allow the probe tip to bend in multiple directions, creating superior control when navigating around corners or complex geometries.
- Non-articulating borescopes maintain a fixed straight design and are ideal for straightforward inspections without directional changes.
Selecting between these types depends on the required viewing angle, accessibility of the inspection area, and the complexity of the equipment being examined.
Technological Advancements in Borescopes
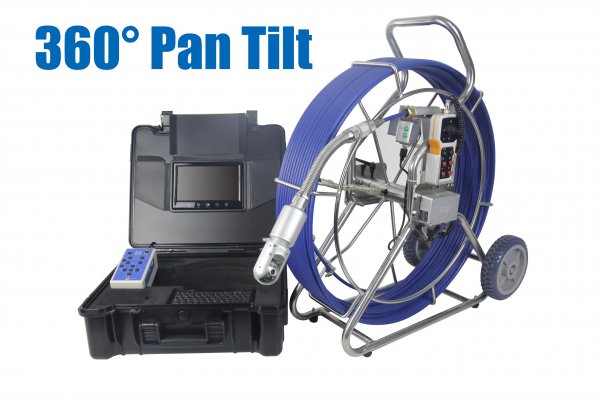
The evolution of borescope technology has significantly enhanced inspection capabilities. Modern borescopes now feature Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor (CMOS) sensors, offering a cost-effective alternative to traditional CCD sensors with improved performance and lower power consumption. Furthermore, dual-camera systems have emerged as a groundbreaking innovation, equipping a single probe with both frontal and side-view cameras. This dual perspective enables inspectors to effortlessly switch between views, ensuring a comprehensive examination of the inspection area.
Applications & Real-World Use Cases
Borescope inspection cameras are not limited to one field—they are everyday tools across different situations where visibility matters. Some of the most common scenarios include:
- Automotive maintenance: Quickly check engine cylinders, valves, or fuel systems without dismantling major components.
- HVAC systems: Inspect ducts, evaporators, or coils for blockages or corrosion to restore efficiency.
- Plumbing & drains: Locate clogs, cracks, or leaks in pipelines, even under wet conditions, with waterproof probes.
- Industrial machinery: Assess gearboxes, welds, and cast parts to detect early signs of wear and prevent costly downtime.
- Home repair: Explore behind walls or inside appliances to identify hidden issues before they escalate.
By offering a clear view in hard-to-reach places, a borescope inspection camera helps users—from professional technicians to DIY enthusiasts—work faster, safer, and more cost-effectively.
What is the depth of field in a borescope?
Borescopes, fiberscopes, videoscopes, and pipe cameras have a depth of field, also known as focal distance, which determines the distance from the instrument's tip where a clear image can be obtained. Typically expressed as a range, like 3 to 9mm, if the tip is within 2mm, the image becomes blurry, and if it's beyond 9mm, it becomes too grainy to be of practical use.
What is the difference between borescope and endoscope?
An endoscope is a more advanced version of a borescope. Although they share similar functions, endoscopes are commonly employed in high-risk environments and have a flexible long cable that connects to a miniature camera, enabling maneuverability in extremely tight spaces.
Both borescopes and endoscopes come with integrated LED lights, ensuring proper illumination and maintaining clear visibility for the camera.
What is a borescope used for?
Borescopes are regularly used for industrial systems and equipment that require the need of non-destructive testing. The main reason for these areas is because they are inaccessible by other ways. For example, the visual inspection of engines, turbines, automotive, endoscope and industrial manufactured parts, which require peculiar attention because of their need for safety, maintenance and quality. By and large, borescopes serve a large quantity of applications, which includes power generation, refining, electronics, law enforcement, weaponry, automotive, aerospace, aviation, etc. The listed below are some common areas that need borescope to inspect:
- Turbine Engines: Aircraft Turbines, Motors, Land-Based Turbines, Wind Turbines
- Pipes: Mining & Exploration Maintenance, Oil & Gas Maintenance, Drain/Sewer/Pipe
- Heat exchanger tubes: Co-Gen Plants, Heat Exchangers & Boilers, HVAC and Mechanical
- Gear boxes: Bearings & Gearboxes
- Foreign Object Retrieval: Airframe Inspections
- Cast Parts: Electronic Assemblies, Metal Castings
- Manufactured or machined parts: Engines
Without borescopes for critical internal inspections of machinery and components, objects would have to physically disassemble parts of the plant. This would lead to significant costs in terms of labor, downtime and lost productivity.
Borescopes & Endoscopes in Inspection & Analysis Tools
Borescope inspection
To view invisible areas, borescopes are optical tools without damaging items. There are some advantages of borescopes. The first one is the accuracy of measurement. For many industries, they require accurate capability to position while some need comparison measurement. Secondly, borescopes make inspection more consistent and efficient. Lastly, borescopes keep you connected with wired or wireless communications to PCs, computers, networks and other devices.
Generally, borescopes are composed of these components, including rigid or flexible working length, optical system, sources of light, and tools to view the image. As for application, borescopes are used in many industrial procedures but they are particularly used in gas turbine inspection. In other words, borescope Inspection is really essential to a gas turbine inspection. Operating at much higher temperatures than other turbines, such as steam turbines, the procedure of gas turbines can be very dangerous. The reason why borescopes are crucial to the inspection of gas turbines is that borescopes help these gas turbines to be inspected in a safe way. By doing so, these inspections with borescopes can effectively prevent accidents from happening because of astounding heat from gas turbines. At the same time, they can identify unknown problems inside the machines as well. As a result, they help reduce the cost of repairs and unexpected workplace injury.
By minimizing teardown and standardizing inspection workflows, teams cut unplanned downtime and document issues with photos/videos for traceability.
What is a borescope camera?
When it comes to borescope cameras, there are some common types to tell, including rigid borescopes, flexible borescopes (also known as fiberscope cameras) and semi-flexible borescopes. For rigid borescopes, they are commonly utilized in areas that have direct access because they lack flexibility. As a result, compared to the other two borescopes, the cost of rigid borescopes are the most affordable ones.However, they are usually used for rigid type because the photos out of rigid borescopes are clear. As for flexible borescopes, even though they can’t provide the same quality photos as rigid borescopes, they are helpful devices to reach objects that are hard to reach. Hence, flexible borescopes cost the most among the three types. Nevertheless, flexible borescopes are not common in some areas that require high image quality and high cost. Lastly, it’s semi-flexible borescopes. They do not cost as high as flexible borescopes and they offer better quality pictures than flexible borescopes. Usually, semi-flexible can be used to operate the minimal manipulation for inspection in small tubes. All in all, it’s important to know what kind of borescopes you truly need. What kind of borescope and size of borescope best suit your needs? What is the most suitable length of the borescope for you? They are all the essential questions you should ask yourself while making your choice to purchase.
Types of borescopes
-
Rigid Borescopes: Rigid borescopes transmit apparent and high-quality images. Owing to lack of flexibility and limited movement, rigid borescopes are more cost-efficient and are commonly utilized in areas where entry paths are straight.
-
Flexible Borescopes: Different from rigid borescopes, flexible borescopes are more advantageous if the areas are inaccessible and challenging. Besides, flexible borescopes cost more than rigid borescopes. Inspectors commonly use flexible borescopes for versatility and efficiency.
-
Semi-rigid Borescopes: Semi-rigid Borescopes are an improvement from rigid borescopes. Semi-rigid borescopes share some similarities with flexible borescopes. For instance, semi-rigid borescopes allow users to conduct the minimal manipulation for inspection in small tubes.
-
Micro Borescopes: Micro Borescopes are aimed to inspect extremely narrow areas. Equipped with semi flexible probes, micro borescopes are available to inspect various curves and corners. In addition, due to probe fields being easier for users to replace, it decreases the downtime and improves efficiency.
Different types of borescopes cater for different situations. Each OME-TOP borescope will have its own specific inspection probe for use. You can learn more instructions and specifications from different product pages based on your needs.
Flexible vs. Rigid vs. Semi-Rigid: Exploring Video Borescope Probe Options
Selecting the correct video borescope probe type is essential for achieving accurate and efficient inspection results, as each probe structure behaves differently in confined or complex environments—and probe diameter further determines whether the device can physically access small openings or maintain image quality in larger cavities. Rigid video borescope probes provide high optical stability and mechanical durability, making them suitable for straight-line inspections where the access path does not involve bends or obstructions. Their typically larger diameters also support superior lens clarity and structural strength.
Flexible video borescope probes utilize braided or soft-metal constructions combined with an integrated camera sensor to deliver real-time video feedback while navigating curved, obstructed, or complex pathways inside machinery or piping systems. Smaller-diameter flexible probes allow entry into tight apertures, while mid-diameter configurations offer a balance between maneuverability and image resolution.
Semi-rigid video borescope probes combine controlled stiffness with limited bendability, enabling precise insertion into narrow, linear passages—such as conduit channels, wiring routes, or small-diameter tubing—where flexible probes may over-bend and rigid probes may not fit. Their moderate diameters make them practical for tasks requiring both stability and slight directional adjustment.
Understanding the functional differences—and the role of probe diameter—helps technicians select the video borescope configuration that best aligns with the inspection environment, improving both diagnostic precision and operational safety.
Borescope technology
In order to improve more precise monitoring and more stable maintenance, the technology of borescopes keeps advancing. By doing so, users can effectively lower repair costs during unscheduled downtime.
The first one is Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductors (CMOS). CMOS becomes more and more affordable with a few hundred dollars to get . Historically, CCD image sensors are the common one but now because of advanced technology, CMOS increases performance with lower cost and makes it competitive to make changes to systems with older CCD image sensors. The second one is the upgrade of measurement. In recent years, borescopes have been capable of measuring smaller defects. Hence, in terms of the need of quantifying, it’s a great step, especially for aircraft turbines because they can be kept in a longer time than they could in the past. The last one is the relay lens system. And thanks to Gradient Lens Corporation, it made the relay lens system(the core of borescope design) even easier and less costly. More interestingly, dual-camera borescopes have been a great innovation recently. There are two cameras on one probe. In general, one camera is front view and 0 degree while the other one is side view and 90 degree. Both of the cameras have lighting separately and users can switch the view directions with merely one button.
Dual-camera probes (front + side) let operators switch views instantly to capture both axial and lateral defects in a single pass.
Key Features & Benefits of Modern Borescopes
Modern video borescopes include high-resolution cameras, adjustable LED illumination, articulation control, interchangeable tubes, video recording, and still-image capture. Advanced imaging enhancements such as high-dynamic-range processing, improved noise suppression, and enhanced sensor sensitivity ensure clarity in low-light or high-contrast environments.
Some systems also support 3D measurement or precision defect sizing for crack length, corrosion depth, or wear analysis.
Workflow tools like menu-guided inspections, automated file tagging, wireless synchronization, and structured reporting simplify documentation and improve traceability.
For demanding environments, reinforced housings and sealed controls protect against shock, vibration, dust, and moisture.
How to use a borescope?
Borescopes are regularly used for industrial systems and equipment that require the need of non-destructive testing. Using a borescope makes it possible for you to inspect the narrow and cramped areas. Since a borescope can provide an easier way to see into internal working, there are several kinds of applications, including the inspection of aircraft, motors, and industrial machinery.
Applications of Borescopes – Heat Exchanger Inspection
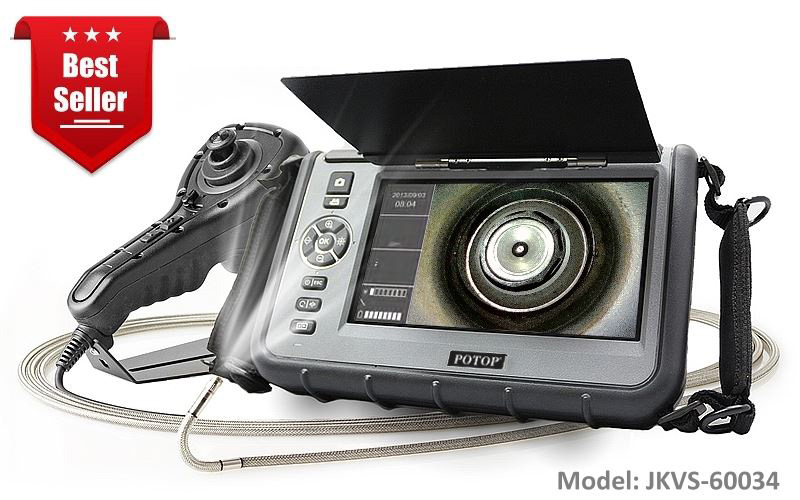
Borescope can assist the inspection of heat exchangers. Heat exchangers can be adversely affected by loose debris, corrosion, pitting, leakage, etc. Reliable operation of systems using heat exchangers mainly depends on the health of components. When equipment wear occurs, it needs to be addressed right away. Otherwise, minimal damage may decrease the efficiency of functioning. JKVS-60054 / JFVS-60054 / CT5-60054 Series articulating borescope allows you to correctly inspect systems.
Utilizing borescopes can help identify any cracks and leaks before catastrophic system failure. If the wear of heat exchangers is caught on time, it is completely fixable. Periodic equipment inspection with a borescope can help repair any cracking and reduce the cost of changing a new machine.
Application of Video Borescope – The Automotive Industry of The New Energy
Since environmental issues are gaining more attention nowadays, the traditional automobile industry has been replaced by environmentally friendly vehicles recently. Industrial video borescopes (or electronic video endoscopes) can be used to observe the interior of equipment or components without disassembly or damage. Hence, industrial video borescopes are widely used in the internal inspection process of traditional automobile engines, tubes, castings and other various parts.
The reason why industrial video borescopes are also called electronic video endoscopes is that electronic video endoscopes are variants of industrial level endoscopes. Moreover, in the field of manufacturing and maintenance of new fuel-efficient vehicles, video scopes are gradually being used in various applications, such as battery detection.
To be more specific, the major components of the battery are the management system, thermal management system, evaporator, ventilator, air duct, etc. The video borescopes can be applied to the detection of battery packs of new energy vehicles, and the probes can enter the inside of the battery pack for effective surface observation, which is more convenient for batch inspection and quality management. In the production and manufacture for new energy vehicles, a large number of procedures are often produced by die-casting process. Thanks to the video borescopes, loosening of the surface, cracks, sand, air bubbles and other defects caused by the casting process can also be efficient. On the whole, an appropriate tool in the service process is also an important test equipment for quality control of new fuel-efficient vehicles.
As stated above, the applications of borescopes are numerous. You are welcome to contact OME-TOP if you need more information.

Industry-Specific Applications
Borescopes are invaluable across various sectors, each with unique requirements. In the aerospace industry, for instance, borescopes play a critical role in inspecting turbine engines for cracks, wear, and foreign object damage (FOD), ensuring the safety and reliability of aircraft. In the automotive sector, they are used to examine internal engine components, helping to diagnose issues without disassembly. Similarly, in the energy sector, borescopes inspect wind turbine gears and blades to prevent failures that could lead to costly downtime.
Specialized Applications
Beyond traditional inspections, borescopes facilitate tasks like foreign object retrieval, crucial in aerospace for removing debris from sensitive areas without dismantling. In manufacturing, they inspect cast parts and machined components for defects such as cracks and misalignments, thereby maintaining high-quality standards and preventing potential failures.
How much does a borescope cost?
The price of a borescope varies widely and doesn’t have an exact number. There are many types of borescopes, including Professional Video Borescope Camera 360°, HD Video Borescope Tungsten Probe 360°, 3D Measurement 360° Video borescope, Cleaning Gun Videoborescope, and so on. Different external factors influence the price of a borescope, since a borescope comes in diverse shapes, sizes,and with a wide range of capabilities.
Generally speaking, the market price of a borescope is roughly between $100 to $60,000. The cost mostly depends on users' needs and budgets. The more additional or customized features you require, the higher price of a borescope becomes.
Furthermore, repairing inspection equipment sometimes costs more than purchasing a brand new borescope. When making a decision on a borescope, it is essential for users to take into account the ruggedness of the scope and potential repair costs or warranties.
HD Video borescope Tungsten Probe 360°
Choosing a Borescope: Guide and Considerations
The main features of the borescope you may emphasize are based on your application. You should consider its articulation, portability, length, diameter, field-of-view, and image comparison when choosing a borescope.
- Articulation: Articulation is vital to guarantee that the full internal surface area is carefully examined.
- Portability: Borescopes with higher portability may be suitable for comprehensive inspections.
- Length: Considering the extensions of the probe length when using the borescope for certain models.
- Diameter: Measuring the size of the entry path. Smaller diameters of probes are easier to get into narrow spaces, while they may be less brighter and cost more.
- Field-of-view: Different cameras are aimed at different sizes and depth of the viewing area.
- Image Comparison: Rigid borescopes can transmit images with higher clarity and durability.
Cost vs. Performance
The cost of a borescope is directly tied to its features, functionalities, and the technology it employs. While high-end models offer superior image quality and advanced features such as dual-camera systems and higher IP ratings, not every inspection necessitates such sophistication. Balancing the cost against the specific requirements of the inspection task is crucial for making a cost-effective purchase decision.
Maintenance and Durability
Proper maintenance extends the lifespan of a borescope. Regular cleaning, careful handling, and adherence to storage guidelines prevent damage and ensure the device remains in optimal condition. Understanding the warranty and available repair services is also vital, as this can significantly affect the total cost of ownership over the borescope's lifecycle.
6 Key Guidelines for Proper and Safe Borescope Use
Industrial video borescopes are indispensable for non-destructive inspections across aerospace, automotive, energy, and manufacturing fields. However, ensuring safety and equipment integrity is crucial during every videoscope inspection. Below are six key points to follow:
- Never use a video borescope on humans or animals — these tools are strictly for industrial applications, not for medical or veterinary use.
- Avoid operating around active machinery or live electrical equipment — inspections should only be performed on powered-off systems to prevent electric shock or mechanical damage.
- Keep away from hazardous environments — do not use or store your video borescope in explosive, high electromagnetic, or flammable atmospheres, as it may trigger fires or system malfunctions.
- Handle the probe with care — avoid over-bending, twisting, pulling, or coiling the insertion tube, as it may lead to internal wire damage, short circuits, or fire hazards.
- Protect your vision and the lens — never stare directly into the probe's LED light, and ensure proper lighting control during use to avoid glare and eye strain.
- Maintain and clean after use — always clean the tip of your video borescope after each inspection, and avoid exposing it to incompatible liquids to prevent corrosion or performance degradation.
Following these practices not only ensures operator safety but also extends the lifespan and reliability of your industrial video borescope system.
FAQs
What does a Borescope Camera mean?
The term refers to the camera module within the video borescope system—a miniaturized high-resolution sensor affixed at the end of the probe, enabling visual capture of hidden interiors.
What is the difference between a borescope and a videoscope?
A video borescope, also called a videoscope, is a type of borescope that includes a miniature camera and a real-time digital display. It allows users to view live video footage during inspection, and often includes advanced features such as image recording, probe articulation, and adjustable lighting. In contrast, a traditional borescope is a simpler instrument that relies on optical lenses or fiber-optic systems. It does not have live video output or recording capabilities, and the user typically views the image through an eyepiece. While both tools serve the same purpose—inspecting hard-to-reach areas—video borescopes offer greater convenience, clarity, and functionality for modern inspection tasks.
How can I use a Video Borescope?
A video borescope is typically used for inspecting industrial equipment and systems in a non-destructive way. To get started, identify the area you need to inspect—pay attention to factors like depth, size of the entry point, and lighting conditions inside the space. Insert the probe carefully into the inspection area, and use the built-in screen to view real-time images or video. Depending on the model, you may be able to adjust LED brightness, control probe articulation, or capture footage for further analysis. The key to effective use is choosing the right type of video borescope based on your application—whether it’s for engines, pipelines, or machinery maintenance. Selecting the proper probe diameter, length, and functionality ensures better inspection results and safer operation.
What applications are video borescopes commonly used for?
Video borescope cameras are widely utilized in non-destructive inspection of internal environments—such as engines, turbines, pipelines, HVAC systems, castings, and confined machinery—to detect corrosion, cracks, blockage, wear, and other forms of damage.
How can I choose the right borescope for my inspection?
Different borescopes might be used for different applications. If you are determining the ideal borescopes, you can check our YouTube channel for videos of products. You can also submit your question for more details and instructions.
How can I learn more details or services about my borescope purchase?
In addition to visiting our product pages for more applications and specifications, you can send a WhatsApp message or submit your question online. OME-TOP will contact and support you as soon as possible.
What is the difference between borescope and endoscope?
Borescope is an industrial endoscope, endoscope is a medical endoscope—different fields of use.
What is the depth of field in borescopes?
Usually 10–100mm, a few models can be customized as telephoto.
What are the limitations of a borescope camera?
Image resolution, articulation range, depth of field, and lighting conditions can affect inspection quality. Some models lack wireless or recording features. Choosing the right probe diameter, articulation type, illumination level, and output format helps minimize limitations.
Which endoscope is used to visualize internal components?
In industrial use, a video borescope or videoscope is ideal for inspecting components like engines, pipes, and turbine interiors. In medical contexts, flexible endoscopes are used specifically to visualize inside the human body—each tool tailored to its respective environment.
What is the difference between a borescope and an inspection camera?
A borescope is a specific type of inspection camera designed with a slim, flexible or rigid probe that can enter very narrow or hard-to-reach spaces. While all borescopes are inspection cameras, not every inspection camera offers the same level of maneuverability or probe design that a borescope provides.
What is the disadvantage of a borescope?
Some models of borescope inspection cameras may have limitations such as a smaller field of view, shorter cable length, or lower resolution. These factors can make them less effective for very complex or large-scale inspections. Choosing the right model for your application helps minimize these drawbacks.
What camera is best for home inspection?
For plumbing or general home maintenance, a waterproof borescope inspection camera with a flexible cable and at least 1080p resolution is ideal. Models that include multiple probe options or interchangeable heads provide extra versatility for different inspection needs around the house.
Can the inspection camera record and save images/videos?
Yes. Most modern borescope inspection cameras feature built-in recording functions. They can capture both images and videos, allowing technicians to document findings, share results, or keep records for maintenance reports.
Is it waterproof for plumbing inspections?
Many borescope probes are designed with IP67 or higher waterproof ratings. This makes them suitable for plumbing, drain, and sewer inspections where the probe may be submerged in water or exposed to moisture.
Can I connect a borescope camera to my phone or computer?
Yes. Depending on the model, connectivity options may include Wi-Fi, USB, or Type-C. This allows users to view real-time footage on smartphones, tablets, or computers, and also transfer captured photos and videos for further analysis or reporting.
Choose the Right Borescope for your Application
|
Product Name |
Image |
Monitor |
Probe |
Camera |
Snapshot & Video Recording |
Specifications |
|
|
5" HD IPS LCD |
|
Camera Pixels 1,000,000 |
v |
|
|
|
|
5.1" HD IPS LCD |
|
720P HD Camera 1280 x 720 Resolution |
v |
|
|
|
|
Large 7" LCD (800*480) |
|
640 x 480 320 x 240 Resolution |
v |
|
|
|
|
3.5" TFT LCD (320*240) |
|
Camera Pixel 640x480 |
|
|
|
|
|
10.1" HD IPS LCD |
|
720P HD Camera 1280 x 720 Resolution |
v |
|
|
|
CJ9 Series 9" Wifi LCD Pipe Inspection Camera Sewer Drain Vide boreoscope |
|
9" Color TFT LCD Display (Touch Screen for Option) |
|
Camera Pixel |
|
|
|
|
7” (180mm) color LCD |
360° Articulation VGA Probe 6mm (P series) |
Camera Pixel 720 x 480 |
|
|
|
|
|
3.5" TFT LCD (320*240) |
|
Camera Pixel 640 x 480 |
|
LED brightness adjustment |
|
|
|
3.5" TFT LCD (320*240) |
|
Camera Pixel 640 x 480 |
|
|
|
|
|
7” color LCD |
HD PIPE Inspection Probe |
720P HD Camera 1280 x 720 |
v |
|
|
|
|
5" TFT LCD (640*480) |
|
Camera Pixel 640 x 480 |
v |
|
Find Your Perfect Borescope Inspection Camera
From day-to-day troubleshooting to scheduled maintenance, a borescope inspection camera helps teams see clearly, act faster, and document every step. Ready to find the right borescope inspection camera for your work? Whether you need a slim probe for tight automotive spaces, a waterproof option for plumbing, or a high-resolution system for industrial inspections, OME-TOP has a solution tailored to your needs. Contact our team today and let us recommend the best model to help you save time, reduce costs, and improve every inspection task.
Read More:
- The best borescopes and inspection cameras by OME-TOP
- Advantage of 360° Articulation Function Borescope
- What is a Video borescope?